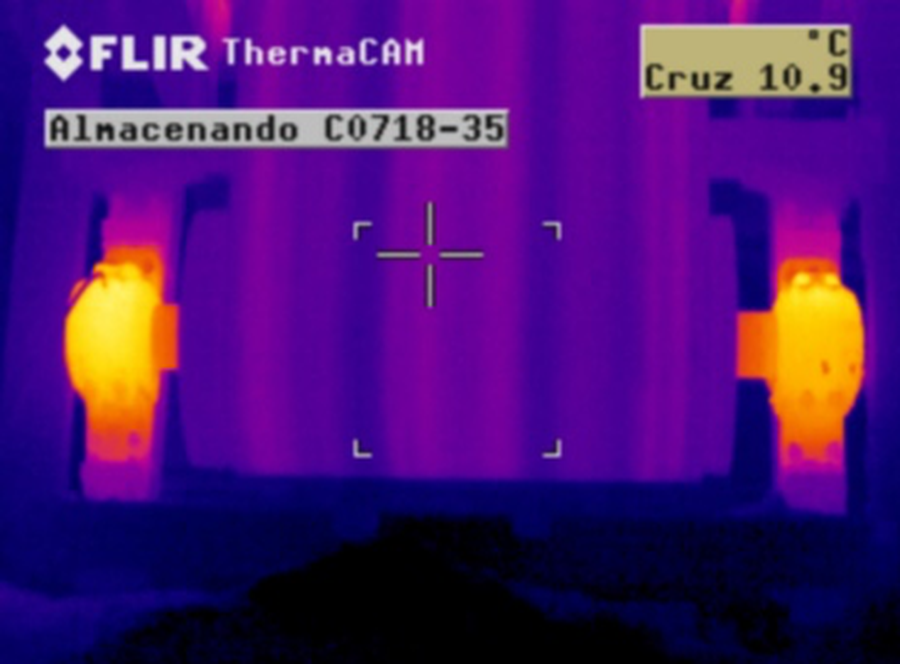
High temperatures refer to the excessive elevation of temperature in components or systems. This failure can be caused by various factors such as excessive friction, overload, lack of lubrication, or issues in airflow. High temperatures can lead to premature material deterioration, reduce efficiency, and in extreme cases, cause severe damage or fires. Infrared thermography is a valuable tool for identifying this type of failure, as it can detect and visually display areas emitting high temperatures in equipment and systems. This allows technicians to identify and address problematic areas before they cause significant damage or hazardous situations.
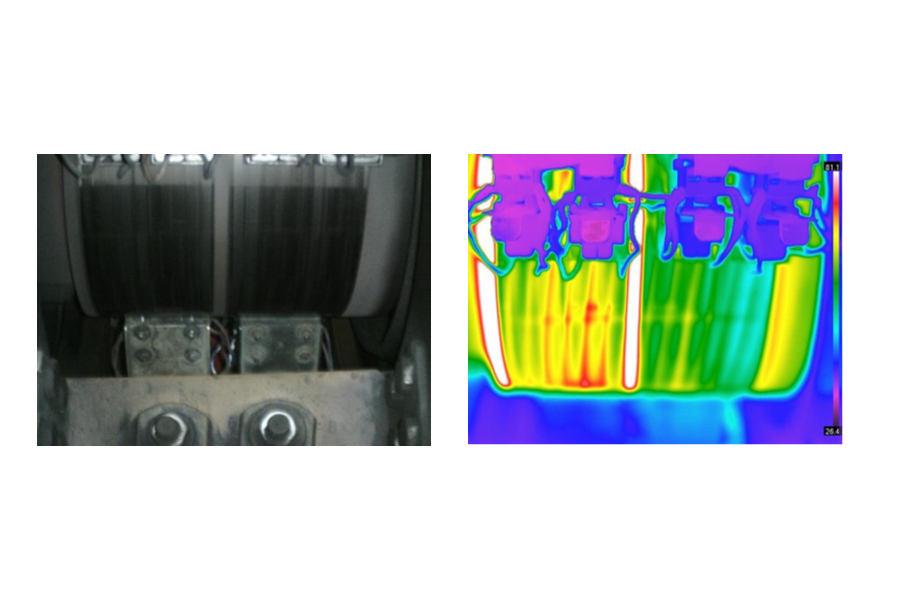
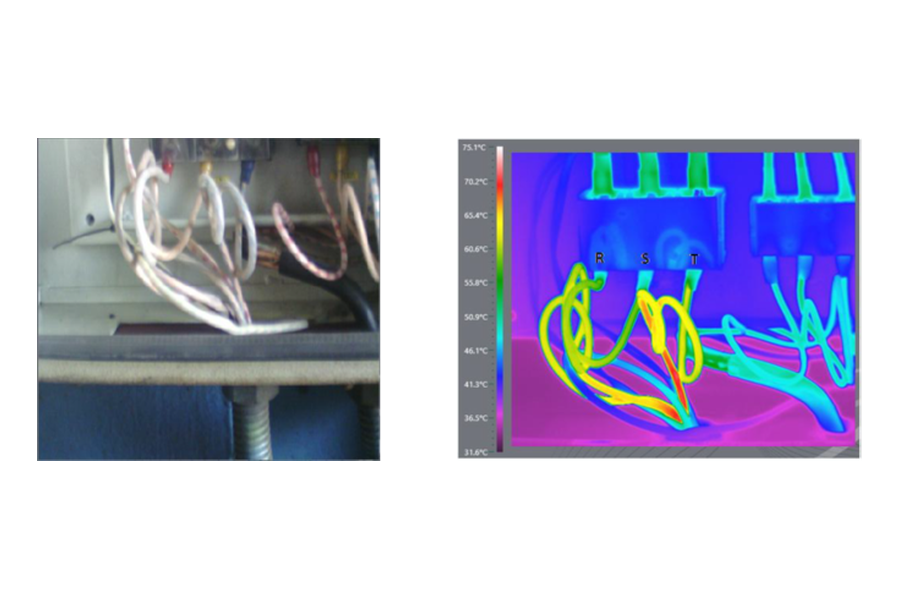
In this case, the measured currents are within normal ranges for the equipment powered by this panel. Therefore, the root cause of the issue might be an incorrect selection of conductors, specifically a diameter smaller than required for the consumption of these devices.
The quantitative analysis shows that the temperatures of the conductors at the terminal entry range between 60 °C and 63 °C. At the terminal exit, where the conductors have a larger diameter, the values range between 51 °C and 53 °C, confirming the hypothesis of the incorrect selection of input conductors.
The temperature values are within the recommended maximum temperature limit for this type of element, which is 60 °C.
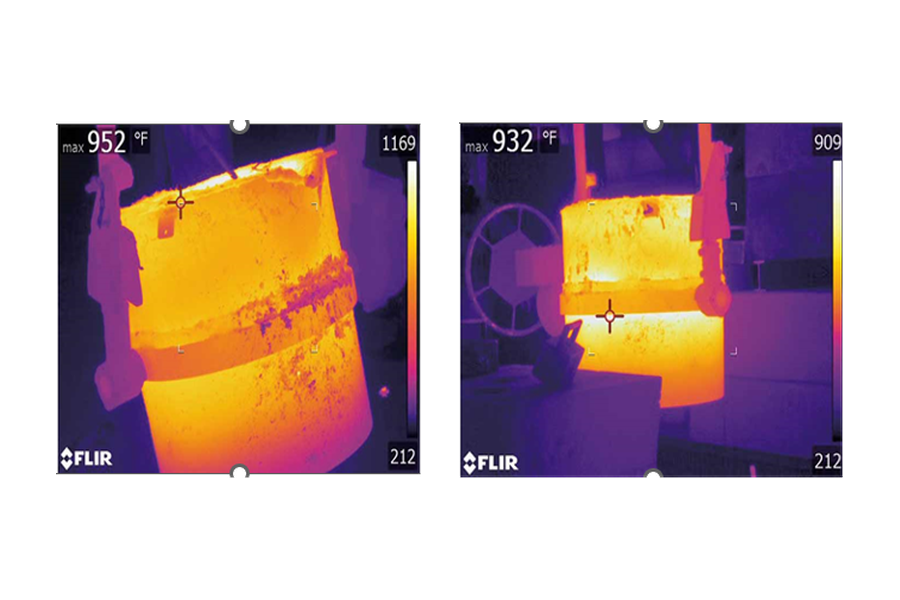
Industrial processes involving very high temperatures, such as the metallurgical industry, chemical industry, and manufacturers of construction materials, require temperature measurements of up to 1200 °C. Infrared thermography enables the measurement of these high temperatures, and for this purpose, it is necessary to select thermographic cameras that allow the addition of optional special filters, high-contrast color palettes, and histogram adjustments.
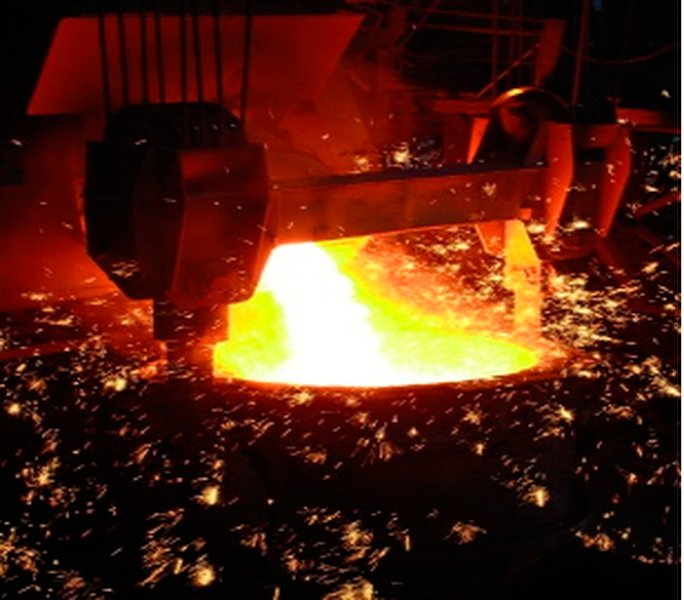

The thermal image provides valuable information for monitoring and controlling process efficiency, detecting potential hot spots or overheating issues, and making decisions to improve productivity and safety in the industrial plant.
In steel mills, it is essential to prevent steel leaks, as they can be extremely dangerous and costly. The temperature involved in the production of cast iron is 1,400 °C (2,552 °F). Infrared thermography allows for monitoring ladles and molds.
Traditional handheld cameras require an operator, limiting the frequency of inspections and creating potentially hazardous conditions in the workplace. Additionally, in these types of processes, hotspots can develop instantly. Opting for online thermography is highly advantageous, as it can detect the early formation of hotspots, distinguishing them from typical splashes, spills, or overflows.
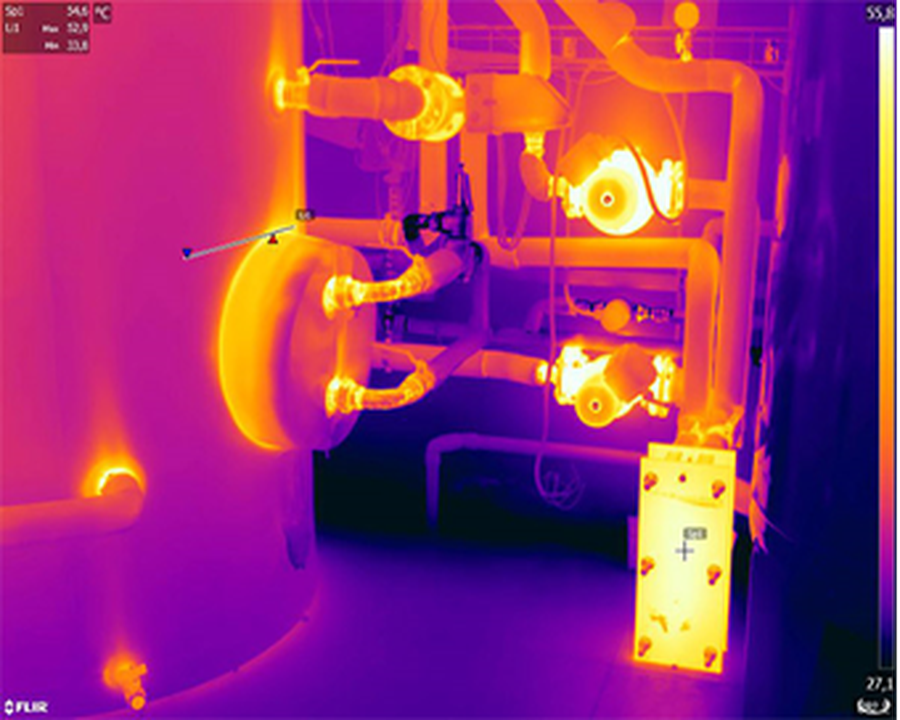
Roller conveyance systems are common in production processes such as paper manufacturing, textiles, laminates, printing, food processing, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and mining. Due to its widespread use, unexpected stoppages in the production process can result in significant production losses. Monitoring these conveyance systems is possible through infrared thermography.

