Guidelines for Conducting Effective Thermographic Inspections
Pre-Inspection Preparation
- Define the inspection objectives and specific areas of interest.
- Review past inspection data and relevant documentation for comparison.
- Ensure that all equipment and cameras are calibrated and functioning properly.
- Consider environmental factors such as ambient temperature and humidity.
Safety Precautions
- Conduct occupational risk assessments.
- Prioritize safety at all times and follow established safety protocols.
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) as required.
- Obtain necessary permits and permissions for accessing restricted areas.
- Do not aim the camera at highly intense energy sources, including devices that emit laser radiation, as reflections from these devices can adversely affect the camera's integrity and may cause permanent damage to the IR detector.
- Avoid looking directly at laser beams, and do not direct laser beams toward people or animals. Be aware that laser beams can reflect off shiny surfaces. Note: After turning on the camera, it performs an internal test, during which the laser pointer is also activated for a few seconds. Do not point it at people or animals until the camera is fully powered on.
- Dispose of defective batteries at a qualified recycling or hazardous waste handling center.
- Take care of the camera to prevent it from falling or receiving impacts, as even minor incidents can affect its calibration.
- Use the camera only as specified in the instructions, as unauthorized use may compromise its integrity, including its calibration.
- Neither the thermographer nor any accompanying personnel should alter or modify any safety cabinets, protective enclosures, or safety interlock systems of the equipment. Any such alterations or breakages should be reported immediately to the person responsible for health and safety at work.

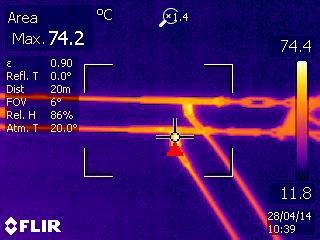
Optimal Environmental Conditions
- Perform inspections during stable thermal conditions for accurate results.
- Avoid conducting inspections under extreme weather conditions or in direct sunlight.
When conducting outdoor inspections on sunny days, heat is added to the inspected elements through the sun's radiation as reflected energy, making it challenging to differentiate severity levels due to increased energy detected by the camera. This can lead to inaccurate temperature calculations and incorrect prioritization of repairs.
On rainy days, surfaces cool down, and water vaporization processes begin, complicating defect severity determination. Severe defects may appear normal due to reduced energy detected by the camera caused by convection.
Similarly, on windy days, air cools the surface through convection, decreasing energy levels in the target area.
The operational and environmental conditions under which data is acquired must be repeatable and consistent with normal operating conditions over time to ensure data integrity and comparability.
Camera Settings and Calibration
- Set the camera to the appropriate wavelength and adjust emissivity settings for accurate temperature readings.
- Perform camera calibration using known reference sources.
- Adjust temperature range and thermal sensitivity based on the target object.
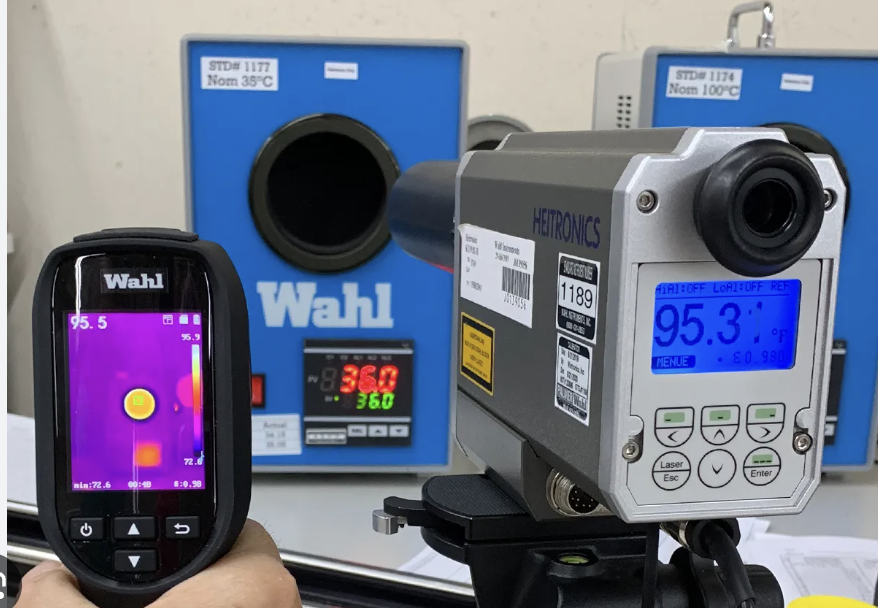

Consistent Imaging Techniques
- Maintain a consistent distance and angle between the camera and the object.
- Ensure proper focus and image resolution to clearly capture thermal patterns.
- Use appropriate lenses for the desired field of view and instantaneous field of view.

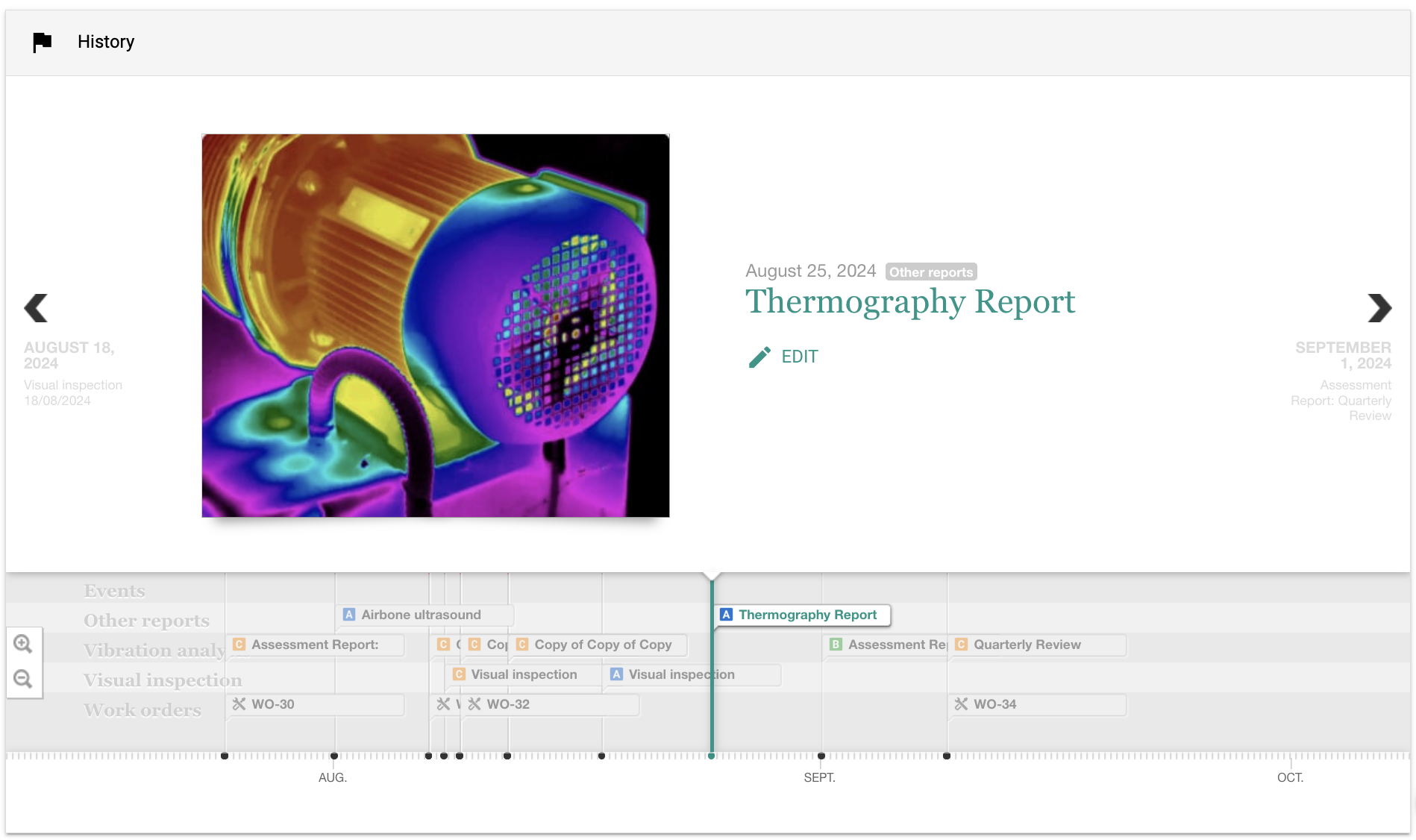
Image Analysis and Interpretation
- Thoroughly review and analyze captured images for potential anomalies.
- Compare temperature differentials and patterns to identify abnormalities.
- Correlate thermal findings with other data to validate observations.
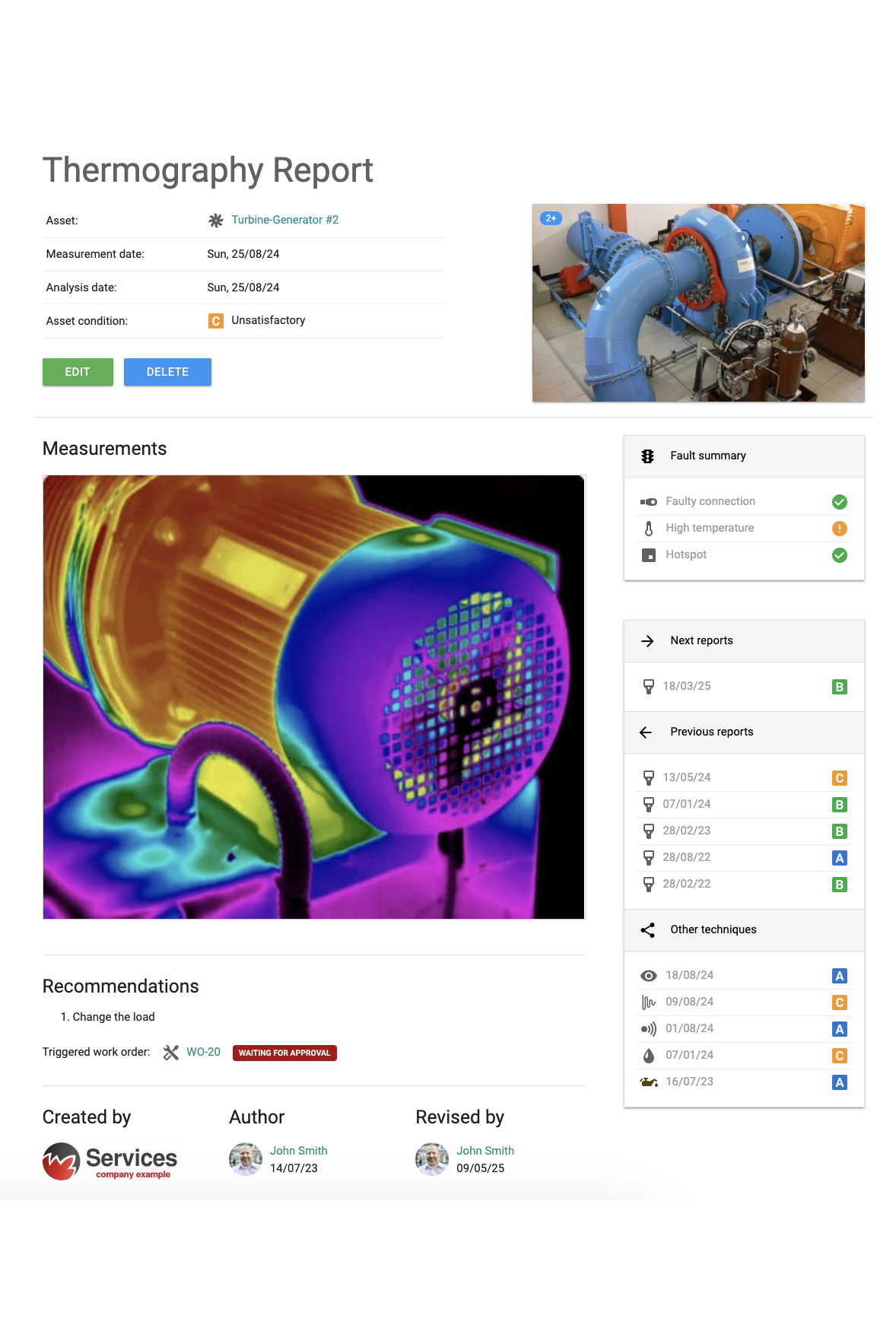
Reporting and Documentation
- Create detailed and well-organized inspection reports.
- Include clear thermal images with annotations to highlight specific findings.
- Provide recommendations for corrective actions based on inspection results.
Ongoing Training and Education
- Stay updated with the latest advances in infrared thermography technology and techniques.
- Engage in continuous professional development to enhance thermography expertise.
Post-Inspection Follow-up
- Monitor the effectiveness of implemented corrective actions.
- Schedule periodic follow-up inspections to track changes and identify new issues.

 cloud_download
cloud_download