Plataformas de gestión en la nube
Las plataformas de gestión en la nube han transformado el mantenimiento basado en condición (CBM) al centralizar datos, automatizar flujos de trabajo y mejorar la toma de decisiones. Estas plataformas integran diversas técnicas de mantenimiento predictivo —como termografía infrarroja, análisis de vibraciones e inspecciones visuales— en un sistema unificado, permitiendo el monitoreo y la gestión eficiente de activos.
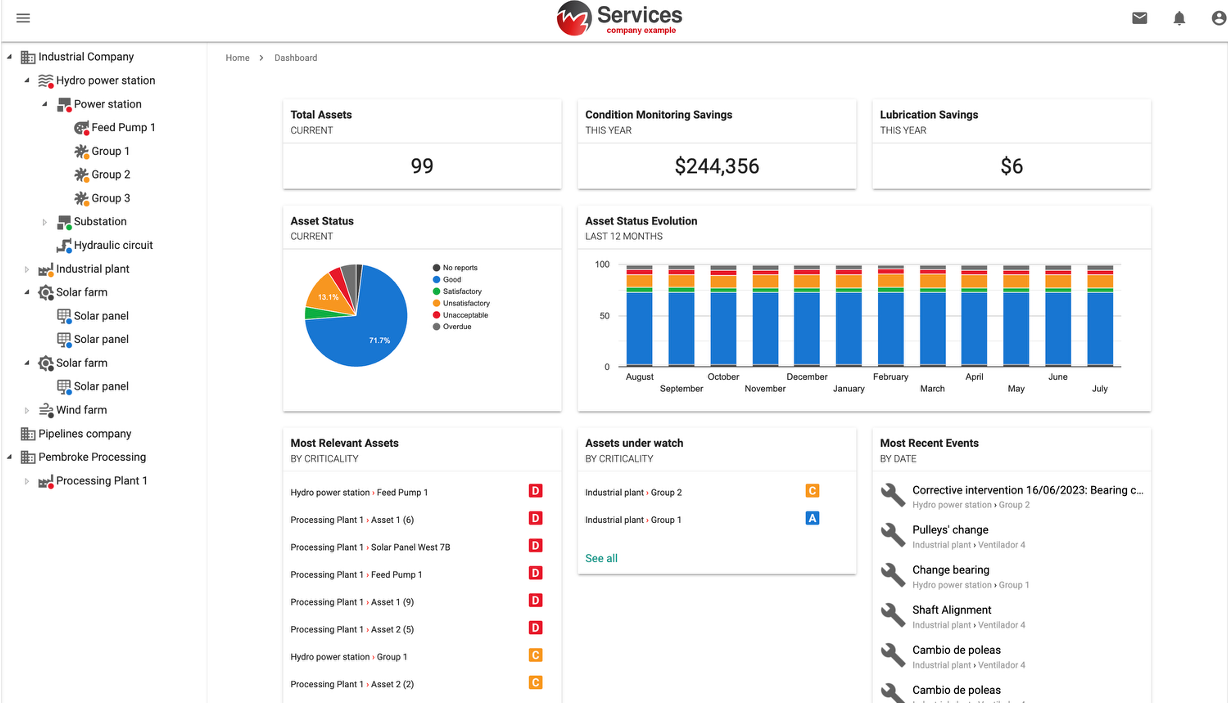
Las principales características de estas plataformas incluyen:
- Reportes automatizados: Generan informes estandarizados a través de distintas tecnologías y marcas de equipos, garantizando consistencia y eficiencia documental.
- Automatización de órdenes de trabajo: Se integran con Sistemas Computarizados de Gestión de Mantenimiento (CMMS) para automatizar la gestión de datos y la creación de órdenes de trabajo, ahorrando tiempo y recursos valiosos.
- Cálculo del retorno sobre la inversión (ROI): Permiten cuantificar y comunicar los ahorros y beneficios derivados de las acciones e inversiones de mantenimiento.
- Análisis causa raíz: Mejoran la confiabilidad de la planta mediante metodologías integradas de análisis, incluyendo mantenimiento proactivo, 5 porqués y diagramas Ishikawa (espina de pescado).
Al aprovechar las plataformas de gestión en la nube, las organizaciones pueden optimizar sus procesos CBM, mejorar la fiabilidad de los equipos y lograr ahorros significativos en costos.
Imágenes multiespectrales
Las cámaras térmicas tradicionales capturan radiación infrarroja en un solo rango de longitud de onda. Sin embargo, la imagen multiespectral permite capturar datos térmicos en múltiples bandas de longitud de onda. Este avance proporciona información más detallada y completa, permitiendo una mejor identificación de distintos materiales y sustancias.

Infrarrojo de alta definición
Con el progreso tecnológico, las cámaras infrarrojas de alta definición son una realidad. Estas cámaras ofrecen mayor resolución de píxeles, permitiendo imágenes térmicas más nítidas y detalladas, particularmente útiles para inspecciones precisas en aplicaciones críticas.
Transmisión en tiempo real
La capacidad de transmisión en tiempo real ha revolucionado las inspecciones termográficas. Con esta tecnología, los datos térmicos pueden transmitirse y visualizarse remotamente, facilitando análisis y decisiones inmediatas incluso desde ubicaciones lejanas. Es especialmente útil para monitorear procesos y equipos en entornos industriales.

Integración de inteligencia artificial
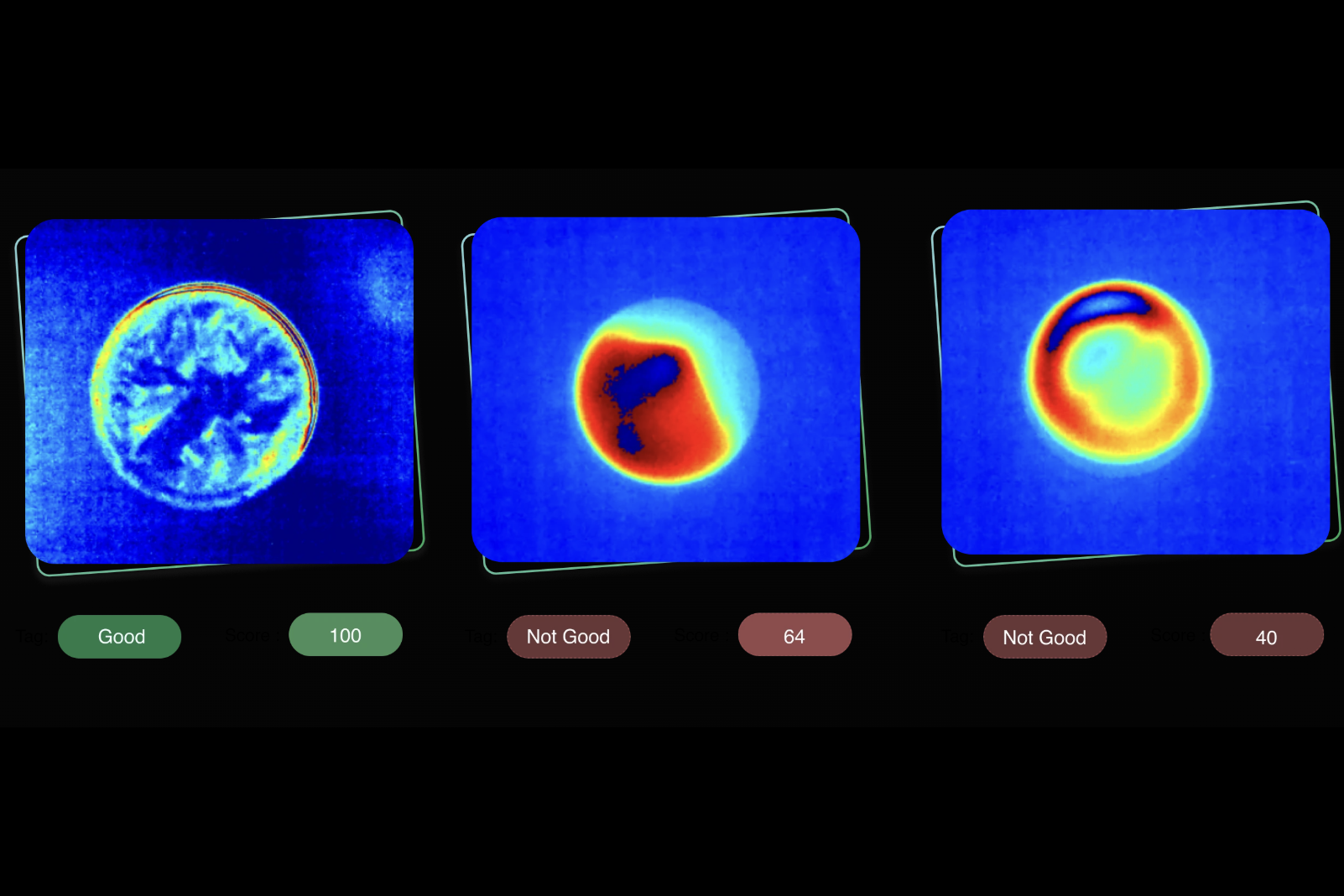
La integración de la inteligencia artificial (IA) en la termografía ha mejorado significativamente el análisis e interpretación de imágenes. Los algoritmos de IA pueden detectar automáticamente anomalías, identificar patrones y clasificar defectos, reduciendo la dependencia de la interpretación manual e incrementando la eficiencia de las inspecciones.
Detectores de matriz de plano focal no refrigerados (UFPA)
Las cámaras térmicas tradicionales requieren mecanismos de enfriamiento para mantener la sensibilidad del detector. Sin embargo, los detectores UFPA funcionan eficientemente sin enfriamiento. Esta tecnología ha facilitado cámaras térmicas compactas, ligeras y rentables, más fáciles de utilizar en diversos entornos.
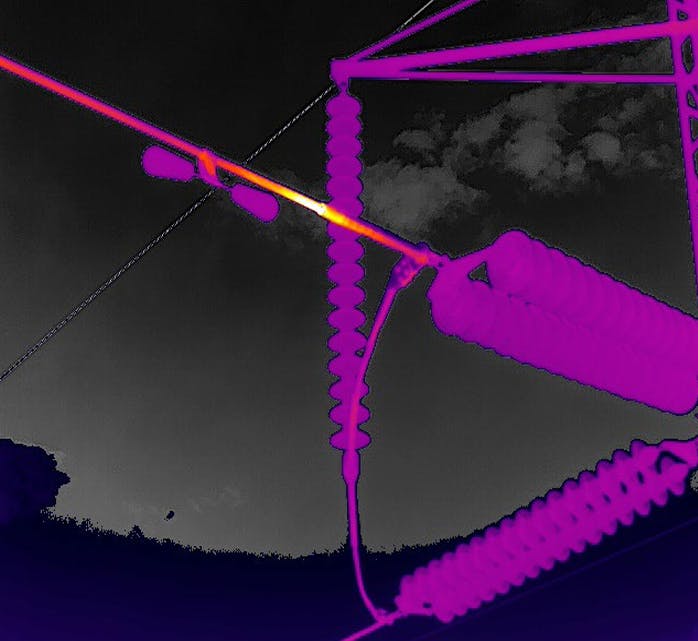
Realidad aumentada (AR)
La realidad aumentada proporciona una manera innovadora de mostrar información térmica en entornos reales. Superponiendo datos térmicos sobre vistas en tiempo real, los termógrafos pueden localizar y visualizar con precisión las variaciones de temperatura, mejorando la interpretación de resultados.

Drones
La integración de cámaras térmicas con drones y vehículos aéreos no tripulados ha ampliado las posibilidades de la termografía aérea, permitiendo inspecciones de grandes áreas, lugares de difícil acceso e infraestructuras anteriormente inaccesibles.
Conforme maduren estas tecnologías emergentes, la termografía alcanzará nuevos niveles de precisión, eficiencia y versatilidad. Adoptar estos avances permitirá tomar decisiones informadas, optimizar procesos y descubrir aplicaciones innovadoras en diversas industrias. El futuro de la termografía infrarroja es brillante, y permanecer a la vanguardia tecnológica será clave para liderar en este campo.

 cloud_download
cloud_download